Why Use Thermal Imaging Camera for Heat Loss Detection
In building energy management, heat loss is a critical factor affecting energy efficiency. Whether in residential, commercial buildings, or cold chain storage facilities, using an infrared camera for energy audit (or thermal imaging camera for heat loss detection) has become the standard method for modern energy audits. Compared to traditional inspection methods, infrared thermal imaging technology can quickly and accurately identify hidden heat leakage issues, helping building owners and facility managers optimize energy costs and enhance operational efficiency.
1. What is Heat Loss and Why Detection Matters?
Building heat loss refers to the phenomenon where indoor heat escapes through building envelope structures such as walls, roofs, doors, windows, and floors. This leakage can stem from various causes, including damaged insulation, poor sealing, or failed pipe insulation. Heat loss issues are prevalent across all building types: from residential homes to commercial buildings, industrial facilities to cold chain warehouses, all face the challenge of energy waste.
The core objective of heat loss detection is to accurately identify hidden thermal leakage points. In ordinary buildings, heat loss drives up heating or air conditioning costs. In cold storage or cold chain warehouses, temperature anomalies caused by insulation failure directly threaten product quality and food safety. By promptly detecting and repairing heat loss issues, all types of buildings can significantly reduce energy consumption and enhance operational efficiency.
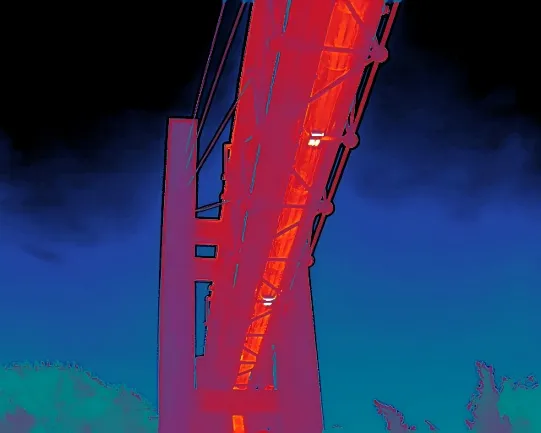
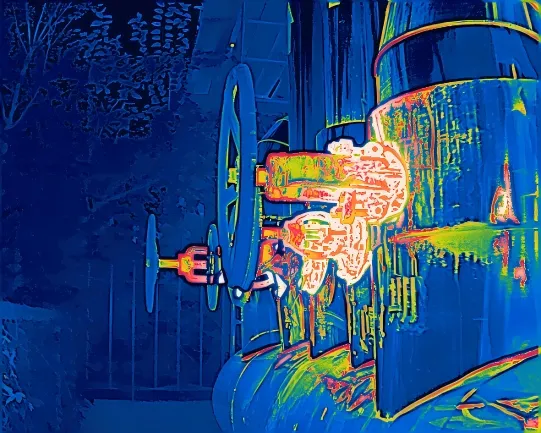
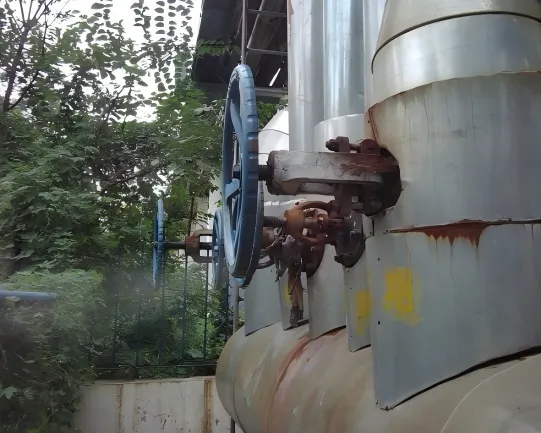
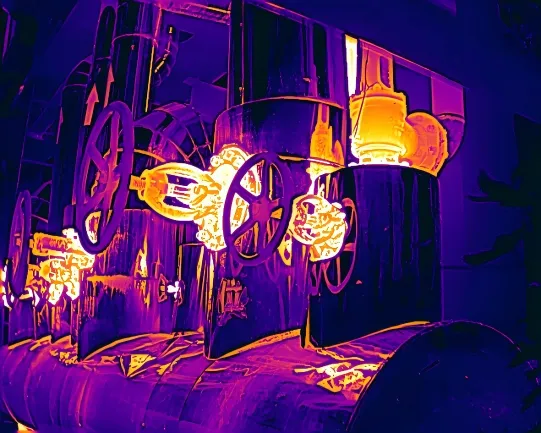




2. How Heat Loss Thermal Imaging Works
A thermal imaging camera for heat loss operates on a fundamental physical principle: all objects above absolute zero (-273.15°C) continuously emit infrared radiation. A thermal heat loss camera captures this invisible thermal radiation, converting it into visual thermal images where color variations represent different temperature levels.
When thermal conduction anomalies occur in building structures, distinct color variations appear in surface temperature distributions. Walls with missing or damaged insulation show as abnormal temperature zones in thermal images; poor sealing around windows also creates noticeable temperature shifts. Such temperature visualization enables inspectors to directly pinpoint heat loss sources, making energy audits both efficient and reliable.


3. Common Heat Loss Issues Detected by Infrared Thermal Imaging
1) Heat Loss in Residential Buildings
① Exterior Wall and Ceiling Insulation Defects
The integrity of a house’s exterior wall insulation directly impacts its thermal performance. When insulation materials are damaged, detached, missing, or improperly installed, heat conduction accelerates through these weak points. During winter inspections, these areas appear as distinct “hot spots” on thermal images, while in summer they manifest as “cold spots.” A thermal camera for house heat loss can rapidly scan entire walls or ceilings to precisely locate insulation defects.

② Door and Window Seal Defects and Air Leaks
Gaps around door and window frames are common sources of heat loss. Real-world inspections typically use a blower door to create a pressure differential between the building’s interior and exterior, forcing outdoor air through gaps into the interior (or vice versa). When air rapidly flows through these gaps, it alters the local temperature distribution. A thermal camera for heat loss clearly displays these “cold flows” or “hot flows,” helping inspectors precisely locate poorly sealed points and providing accurate guidance for subsequent sealing renovations.

③ Underfloor Heating Pipe and Heating System Heat Loss
Poor insulation in underfloor heating pipes or heating circuits results in significant heat loss during transmission. Employing thermal imaging for heat loss detection clearly reveals pipe layouts and heat distribution patterns, quickly identifying leaks, blockages, or insulation failures. Compared to traditional excavation-based methods, infrared thermal imaging enables non-destructive detection, substantially reducing inspection costs and minimizing structural impact.

2) Heat Loss in Cold Chain Storage
① Cold Storage Insulation and Sealing Failures
Air tightness is critical for maintaining stable temperatures in cold storage. Insulation layer damage or poor sealing can cause localized temperature increases, creating dead zones that directly threaten cold chain food safety or product quality. Scanning cold storage walls, floors, and ceilings with an infrared camera for heat loss detection reveals distinct hot spots at insulation breaches. Staff can then conduct targeted repairs at these indicated locations, minimizing cold loss and reducing energy consumption.

② Cold Chain Transportation Temperature Anomalies
When transporting temperature-sensitive goods, poor insulation or sealing defects in cold chain vehicles can cause temperature fluctuations that jeopardize cargo quality. Real-time thermal imaging of the entire temperature distribution within the transport vehicle promptly detects abnormal temperature zones and triggers alerts, ensuring goods remain within specified temperature ranges throughout transit.

3) Heat Loss in Industrial and Commercial Buildings
① Large Building Envelope Thermal Leakage
Commercial buildings and industrial facilities typically feature extensive exterior walls and roofs. Within these large-scale structures, a single insulation defect can accumulate into significant energy waste. Thermal camera energy audit rapidly scans building surfaces to identify poorly insulated areas, roof insulation defects, and temperature anomalies beneath waterproofing layers, providing facility managers with systematic maintenance prioritization.
② Industrial Equipment and Piping Insulation Defects
In industrial facilities, damaged or defective insulation materials applied on equipment like piping, storage tanks, and heat exchangers directly lead to substantial energy waste and increased operational costs. Infrared scanner for heat loss can swiftly pinpoint heat leakage locations on these high-temperature equipment, guiding precise repairs.
4. Advantages of Thermal Imaging for Heat Loss Detection
1) Non-Contact Precise Localization and Root Cause Identification
Thermal heat loss cameras require no direct contact with the target object, allowing operators to work from a safe distance. The system automatically captures the hottest/coldest points across the entire screen or designated areas, visually highlighting problem zones and pinpointing their exact locations. This non-contact, intuitive approach enables rapid identification of heat loss sources, supporting reliable, accurate root cause analysis.
2) Temperature Visualization for Large-Scale Detection Coverage
Thermal images convert temperature variations into visible color distributions. Temperature values can be displayed for any area within the image, offering a comprehensive overview of the building or equipment’s thermal characteristics. This temperature visualization is intuitive and easy to understand, meeting the demand for large-scale inspections of extensive structures and making results straightforward to interpret, document, and analyze.
3) Flexible Temperature Alarm and Timely Warning
Modern thermal imaging systems allow users to set temperature alarm thresholds. When temperatures reach preset ranges, the system automatically triggers alerts so that personnel can promptly identify anomalies and take corrective actions. This proactive warning mechanism ensures heat loss issues are detected and addressed in a timely manner.
4) SDK Support and Multiple Information Transmission Methods
Professional-grade thermal imaging systems provide SDKs for secondary development and feature diverse interfaces including IO ports and serial ports. The system supports flexible alarm notifications (such as SMS, app alerts, and audible/visual alerts) and can be integrated with existing devices, platforms, and systems to deliver comprehensive intelligent management solutions.
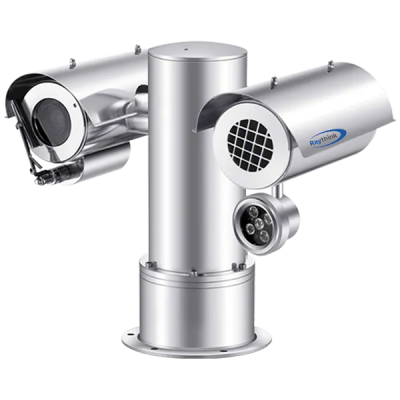
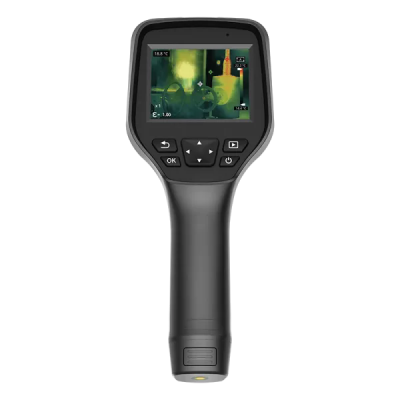
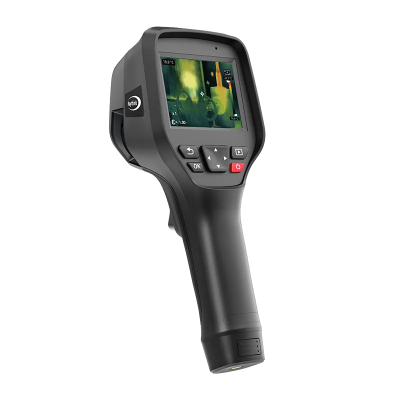
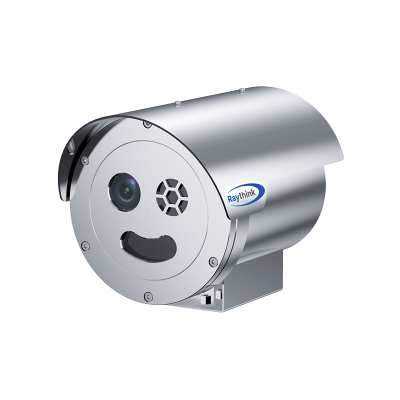
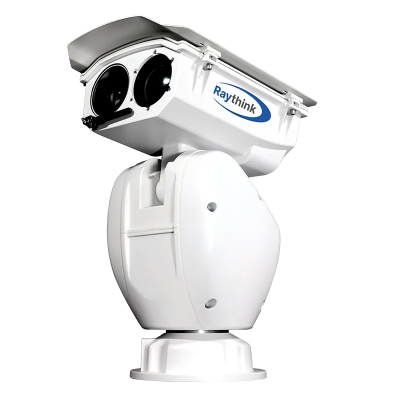
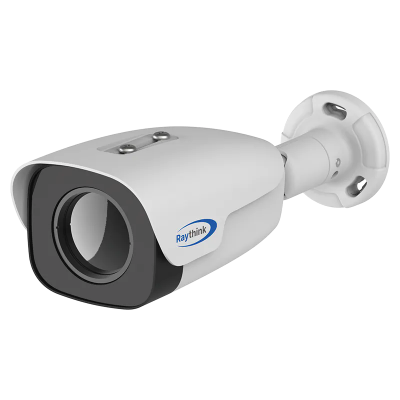
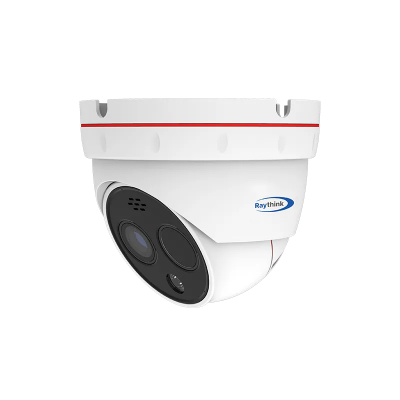
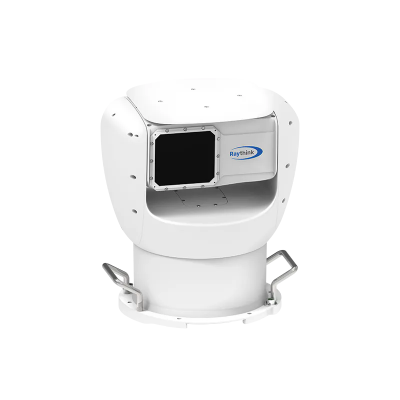
5. Raythink Thermal Heat Loss Camera Recommendations

Recently Posted
-
Making the Invisible Visible: Latest Thermal Imaging Solution for 3D Gas Leak Detection
December 17, 2025According to Markets and Markets™, the Gas Detection Market is expected to reach USD 5.18 billion by 2030, from USD Read More
Read More -
Best Termite Thermal Imaging Cameras From Raythink
December 12, 2025Termites represent one of the most severe pest threats facing the global construction industry. Unlike other pests, the concealed Read More
Read More -
Raythink Thermal Imagers: Precision Monitoring Solutions for Multiple Industrial Scenarios
December 10, 2025In the core links of industrial production, temperature monitoring, explosion-proof security, and process control directly affect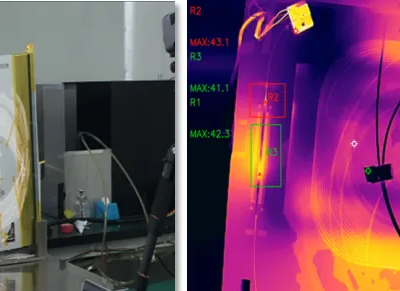 Read More
Read More -
Batteries & Charging Piles: Infrared Thermal Cameras Safeguard New Energy Vehicles
December 9, 2025With the rapid development of the new energy vehicle industry, safety issues related to core components such as power batteries an Read More
Read More























