Application of Thermography In NDT
In industries spanning manufacturing, aerospace, and construction, the safety of equipment and materials directly impacts production efficiency and operational reliability. To promptly detect potential defects without damaging the object, non-destructive testing (NDT) has emerged as a critical method for ensuring quality and safety. With growing demands for faster inspection speeds, broader coverage, and real-time monitoring capabilities, infrared thermography NDT—as a non-contact, rapid, and visual inspection method—is becoming an essential complement to traditional NDT techniques, providing efficient solutions for early detection of hidden defects and abnormal conditions.
1. What is NDT
Non-destructive testing (NDT) refers to inspection and evaluation methods that assess internal and surface defects, structural conditions, or operational status without damaging the structure or performance of the tested object. Common NDT methods include ultrasonic testing, radiographic testing, magnetic particle testing, penetrant testing, eddy current testing, and infrared thermography testing.

2. What Is Thermography Non-Destructive Testing
1) Basic Principles
Thermography non-destructive testing is an NDT method based on the infrared radiation characteristics of objects. All objects with temperatures above absolute zero continuously emit infrared energy. When internal defects, structural anomalies, or thermal property variations exist within an object, its surface temperature distribution changes accordingly. Infrared thermal cameras capture and visualize these temperature differences through non-contact measurement, converting invisible thermal information into intuitive thermal images. This enables analysis and evaluation of both surface and subsurface defect conditions in the inspected target.
2) Testing Methods
Based on whether external heat sources are required, infrared thermography NDT is typically classified into passive and active types.
· Passive Thermography Non-Destructive Testing:
This method utilizes the natural infrared radiation characteristics of the tested object to obtain its surface thermal image and analyzes the thermal image to derive the required information.
· Active Thermography Non-Destructive Testing:
This method introduces external heat to enhance the temperature difference between the object’s surface and its surrounding environment, making it sufficiently pronounced for infrared thermal cameras to detect or improve detection accuracy.
3. Advantages and Limitations of Thermography in NDT
1) Advantages
· Non-Contact Inspection:
Infrared thermography NDT employs non-contact measurement, acquiring surface temperature information without direct contact with the tested object. Inspection is completed without affecting structural integrity or material properties, avoiding mechanical damage, contamination risks, or secondary destruction that traditional contact-based methods might cause. This makes it especially suitable for inspection scenarios involving high temperatures, live electrical systems, rotating equipment, or hazardous environments.
· High Sensitivity:
Thermography non-destructive testing can capture subtle temperature variations caused by internal defects in targets. This high sensitivity to temperature differences gives infrared thermography distinct advantages in early defect identification, quality consistency assessment, and fault hazard prevention, providing strong support for quality control and failure diagnosis.
· High Inspection Efficiency:
Thermography non-destructive testing can capture temperature distribution information across the entire inspection area in a single frame without point-by-point scanning, enabling high-speed inspection and wide coverage. This characteristic makes it particularly suitable for online quality monitoring of large-scale production lines, rapid screening of batch products, and preventive maintenance of equipment, helping shift defect identification from post-event detection to process monitoring.
2) Limitations
· Limited Detection of Deep-Seated Defects:
Infrared thermography essentially reflects the surface temperature distribution characteristics of the tested object. When internal defects are located at considerable depth and do not significantly alter surface thermal conductivity, their manifestation in thermal images may be insufficiently pronounced or even difficult to identify directly. Therefore, for detecting deep cracks or complex internal structures, thermography non-destructive testing typically needs to be combined with ultrasonic, radiographic, or other NDT methods to achieve more comprehensive defect assessment.
· Susceptibility to Environmental Conditions:
External factors such as ambient temperature fluctuations, solar radiation, wind speed, and humidity can all interfere with infrared thermal data, compromising the stability and accuracy of temperature measurements. Real-world applications of thermography non-destructive testing require either controlled environmental conditions tailored to specific operating scenarios or algorithmic compensation and data correction techniques to mitigate environmental impacts on results.
· Requirements for the Surface Condition of Tested Objects:
The surface roughness, emissivity variations, and reflective properties of the test object all directly affect the quality of the acquired infrared radiation signal. Therefore, before conducting thermography non-destructive testing, it is typically necessary to evaluate the surface condition of the tested object and take appropriate emissivity correction measures to improve the reliability of inspection results.
In recent years, with continuous improvements in infrared detector performance, image processing algorithms, and system integration capabilities, infrared thermography NDT technology has developed rapidly, gradually becoming an important complement to traditional testing methods such as laser and ultrasonic testing, and even achieving effective replacement in some application scenarios. Additionally, this technology can be integrated with other NDT methods to further enhance testing accuracy, reliability, and comprehensive diagnostic capability.
4. Applications of Thermography in NDT
1) Aerospace
Thermography non-destructive testing is widely used for inspecting critical components such as composite structures and engine blades in aircraft and spacecraft. It effectively identifies hidden defects including delamination, voids, and cracks. By capturing thermal conduction differences between defective areas and normal materials, infrared thermography NDT achieves rapid inspection under non-contact and non-disassembly conditions, playing a vital role in ensuring aerospace structural integrity and flight safety.
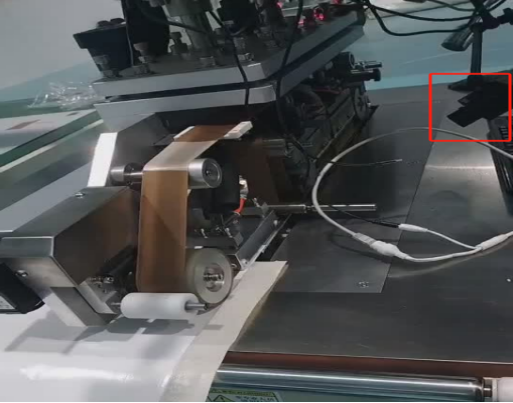
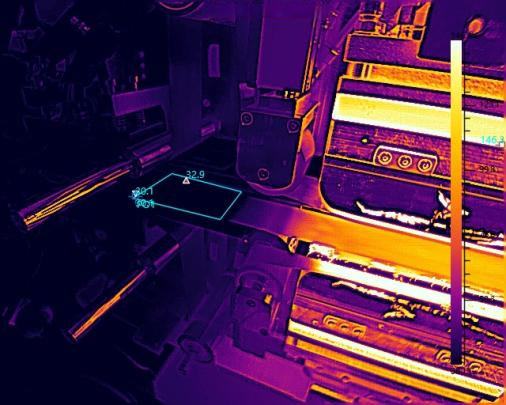


2) Electrical Power Systems
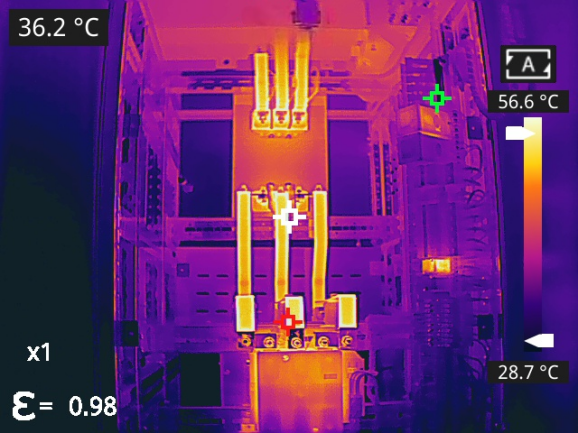
Abnormal heat generated during the operation of electrical equipment is often a direct indicator of faults. Thermography non-destructive testing can be used for online inspection of transformers, switchgear, cables, busbars, and other primary equipment. By identifying localized overheating phenomena, it enables the timely detection of potential hazards like poor contacts, overloads, and insulation aging, serving as an important tool for condition monitoring and preventive maintenance in power systems.
potential hazards like poor contacts, overloads, and insulation aging, serving as an important tool for condition monitoring and preventive maintenance in power systems.
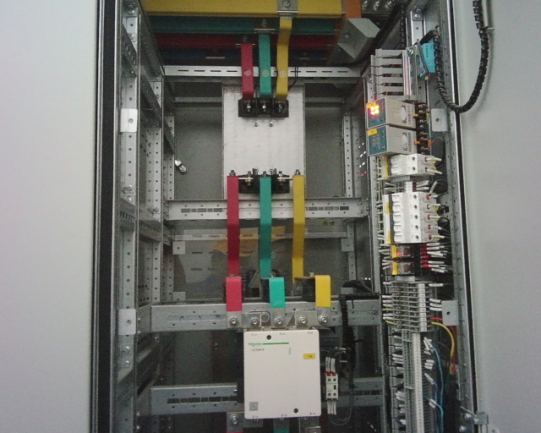

3) Petroleum and Petrochemical Industries
Petroleum and petrochemical equipment operates under high-temperature, high-pressure, and corrosive conditions, posing significant safety risk. Infrared thermography NDT enables non-contact and online monitoring of pipelines, vessels, and reactors, promptly detecting abnormal temperature rises and uneven heat distribution. This provides critical data for equipment health assessment and maintenance decisions, reducing the risk of unexpected failures.


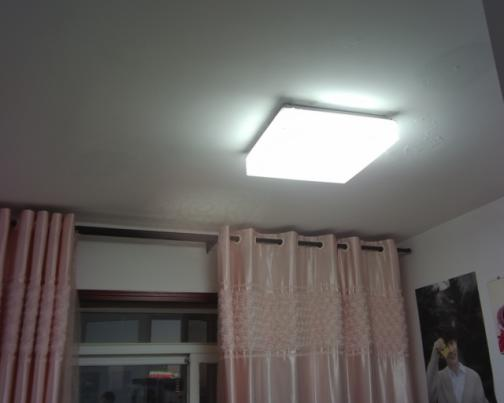
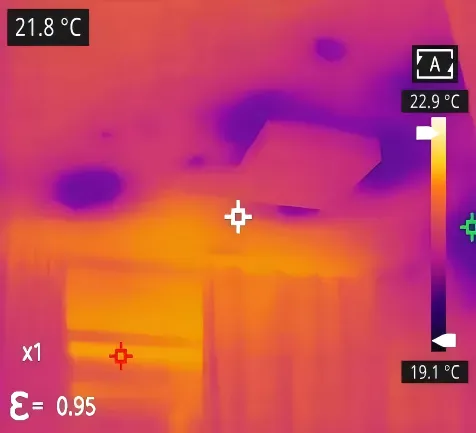
4) Building and Construction
In the construction sector, the application of thermography in NDT is mainly for inspecting building envelopes and HVAC systems. By analyzing building surface temperature distribution, it can assess insulation performance, locate leak points, and identify structural defects. In energy audits and HVAC system inspections, it helps discover thermal bridges and energy consumption anomalies, improving overall building energy efficiency and safety.


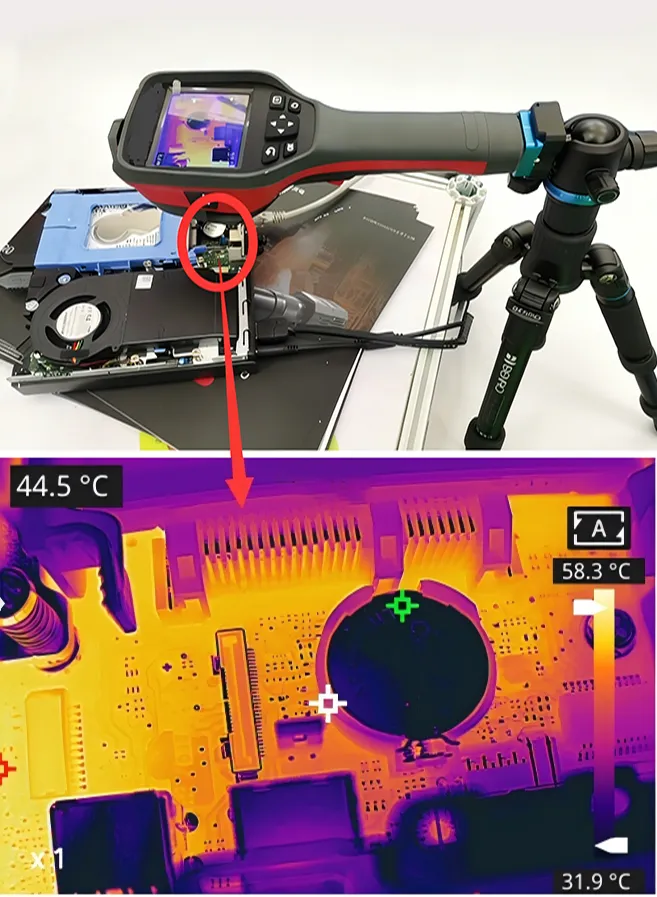
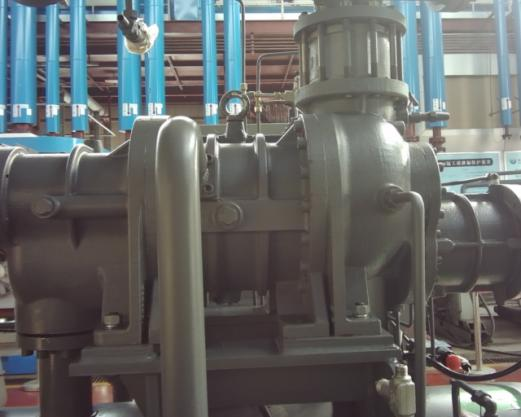
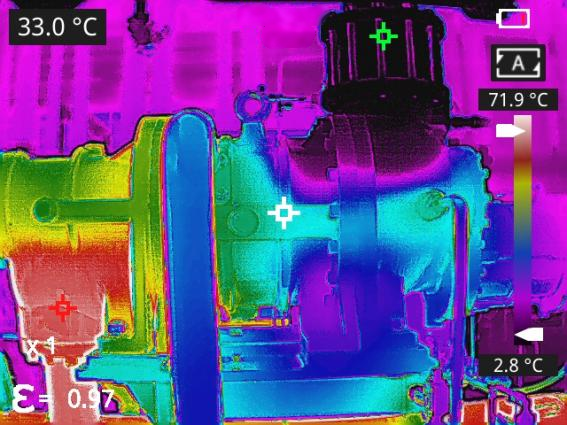
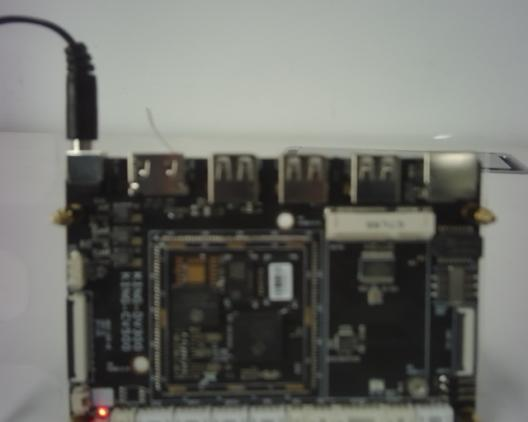
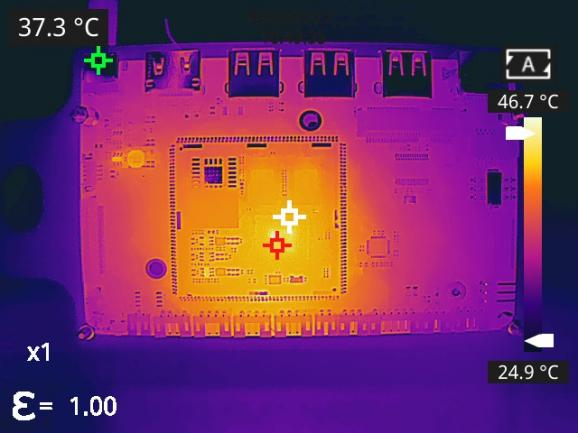
5) Industrial Manufacturing
In industrial manufacturing, thermography non-destructive testing can be used for equipment operation status monitoring, product quality inspection, and energy efficiency analysis. By rapidly identifying equipment hot spots and process anomalies, it enables early fault pre-warning. Combined with product thermal characteristic analysis, it assists quality control and process optimization, improving production stability and energy utilization efficiency.


6) Medical and Healthcare
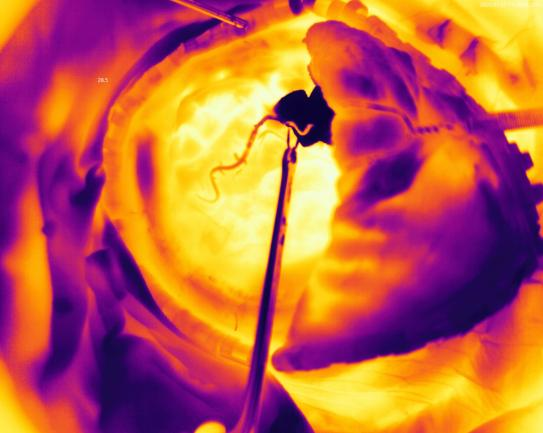
Infrared thermography in the medical field is primarily used for early disease screening and auxiliary diagnosis. Pathological areas in the human body typically feature changes in local metabolism and blood flow, leading to abnormal body surface temperature distribution. Through non-contact detection of the human body’s thermal equilibrium state, it can provide objective reference data for clinical diagnosis and treatment efficacy evaluation.

5. Raythink Product Recommendations

RM600G Professional Handheld Thermal Camera

RT630 Expert Thermal Camera

TN220 Thermographic Cube Camera

AT61 Motorized Focusing Thermal Camera

TN460 Fixed-mount Thermal Camera
6. Conclusion
As a non-destructive testing method utilizing temperature fields as information carriers, infrared thermography is progressively evolving from an auxiliary inspection tool to one of the core technologies in engineering applications. Its non-contact, high-efficiency, and visualization characteristics are transforming NDT from “post-event determination” toward “process monitoring” and “early warning.” With continuous improvements in infrared detector performance, algorithmic capabilities, and system integration levels, the application of thermography in NDT will deliver greater value in more complex operating conditions and critical industries, providing more forward-looking technical support for equipment safety, quality control, and reliable operation.
Raythink provides reliable, user-friendly thermal cameras and comprehensive technical support to users worldwide. If you are exploring the application value of infrared thermography NDT in specific scenarios, or seeking inspection solutions tailored to your operational conditions, please contact Raythink to jointly explore more efficient and reliable NDT practice approaches.
Recently Posted
-
Passive vs. Active Thermography: How Thermal Cameras Enable Different Inspection Techniques
February 5, 2026In power grid inspections, industrial equipment maintenance, and security monitoring scenarios, thermal cameras have bec Read More
Read More -
TN220 Thermographic Cube Camera: Cigarette Pack-Sized Infrared Device Unlocks New Safety Monitoring
February 4, 2026In the field of industrial safety monitoring, three core pain points have long plagued operation and maintenance teams: difficulty Read More
Read More -
What Is The Best Thermal Camera For Electronics Repair and Rework?
February 2, 2026Electronic products face various circuit faults and hidden defects during development, manufacturing, and maintenance. Technicians Read More
Read More -
Outdoor Commercial Security Cameras: What You Need to Know
January 28, 2026In today's complex security landscape, outdoor areas of commercial properties face challenges such as theft, vandalism, survei Read More
Read More























