What Is The Best Thermal Camera For Electronics Repair and Rework?
Electronic products face various circuit faults and hidden defects during development, manufacturing, and maintenance. Technicians need efficient methods to quickly identify problems. Abnormal temperature rise is often a subtle yet critical fault indicator. As a non-contact temperature measurement tool, the thermal imaging camera intuitively displays the thermal distribution characteristics of electronic products, gradually becoming an essential tool for electronics engineers in fault diagnosis, performance monitoring, and reliability verification. This article discusses the necessity, typical application scenarios, and usage best practices of the thermal camera for electronics repair and rework.
1. Why Need a Thermal Camera for Electronics Repair and Rework
Traditional circuit fault detection methods require point-by-point measurement of voltage, current, impedance, and component parameters at critical points and lines, combined with circuit diagram analysis for inference. This process is cumbersome and highly dependent on experience, resulting in low detection efficiency and a high risk of missing faults. It struggles to meet the inspection demands of modern high-density, miniaturized electronic components.
When electronic components fail, such as through short circuits, open circuits, or poor contact, the current flowing through the component is affected, causing the component temperature to differ significantly from its normal state. This makes thermal anomalies the most direct fault indicator of failure. By analyzing the temperature distribution within electronic products, potential hazards can be identified while powered on, discovering problem areas that are difficult for the naked eye to detect, thereby reducing the need for disassembly and repeated verification.
Thermal imaging cameras capture infrared radiation emitted by components, providing a comprehensive temperature view that enables engineers to quickly pinpoint problem areas, significantly improving the accuracy and efficiency of R&D testing and repair work.
2. Best Thermal Camera for Electronics: Raythink Recommendations
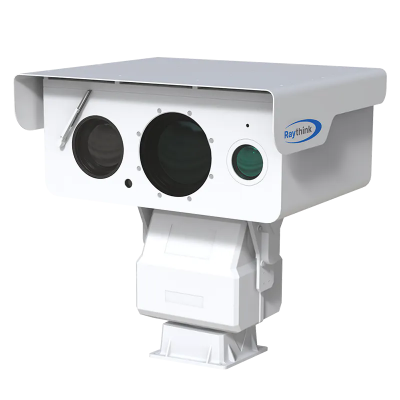
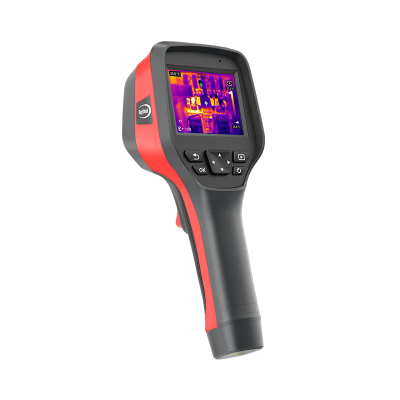
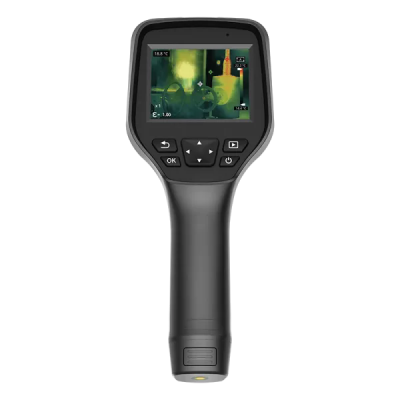
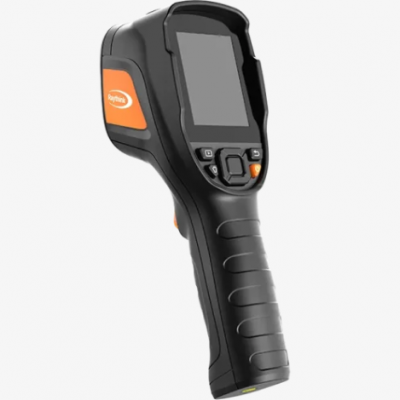
1) RM620 Handheld Thermal Camera
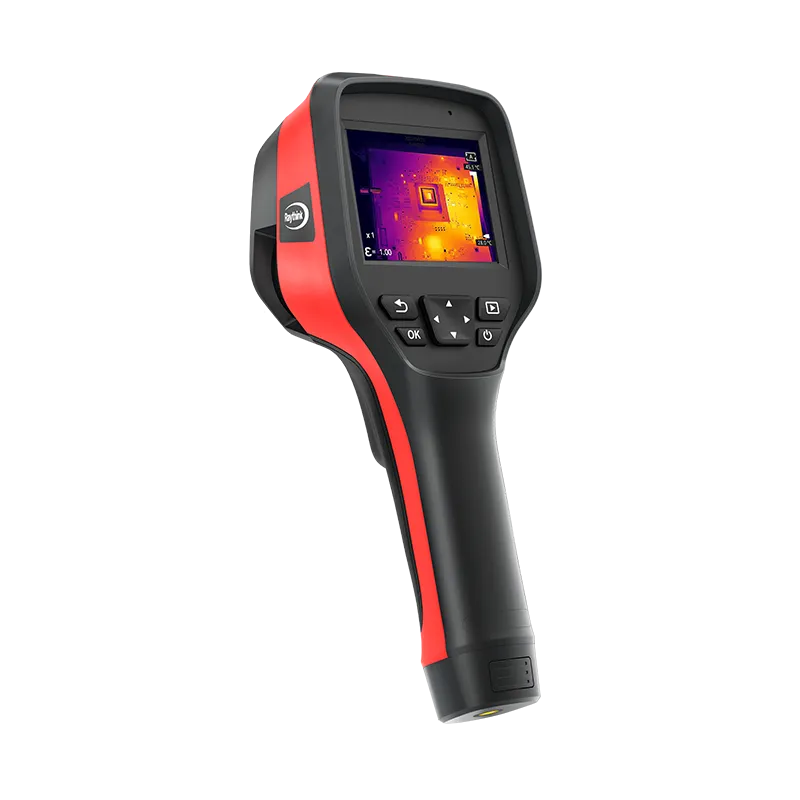

· 640×512 infrared high resolution
· 5-megapixel visible light camera
· Temperature measurement range: -20°C to +650°C
· Smart upgrades: isothermal lines assist in fault analysis and equipment inspection
· Customizable point/line/area temperature analysis with intuitive, clear feedback
· Wi-Fi transmission for mobile app and smart PC analysis software integration
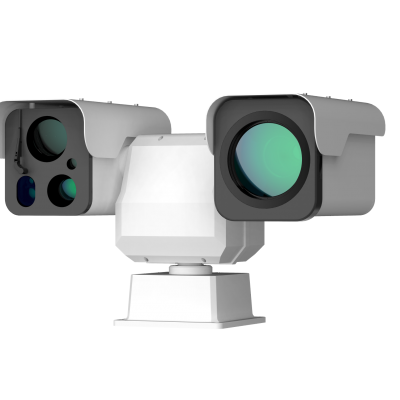
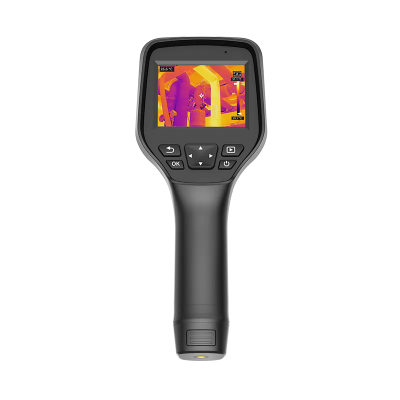
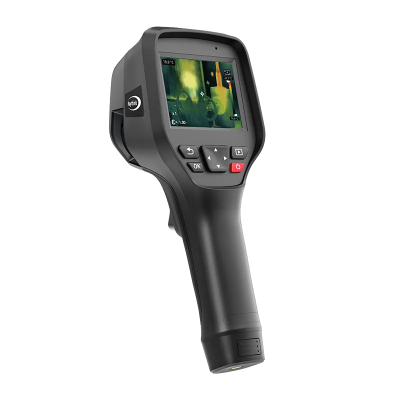
2) AT31 Motorized Focusing Thermal Camera

· Next-generation image algorithm for enhanced detail clarity
· 384×288/640×512 infrared resolution options for high-definition visuals
· <40mK NETD, superior to competing products
· Wide temperature measurement range: -20°C to +650°C
· 50Hz synchronized image and temperature frame rate
· Compact size, low power consumption, multiple lens options
· Rich interfaces with SDK support for easy integration
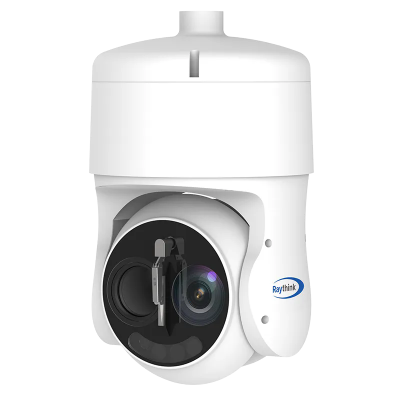
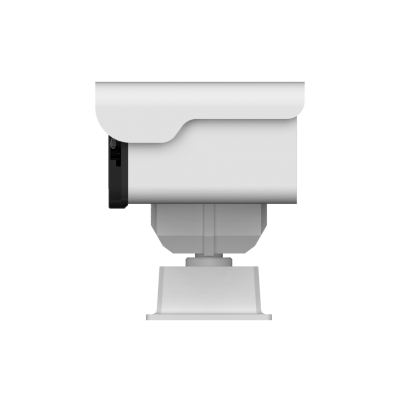
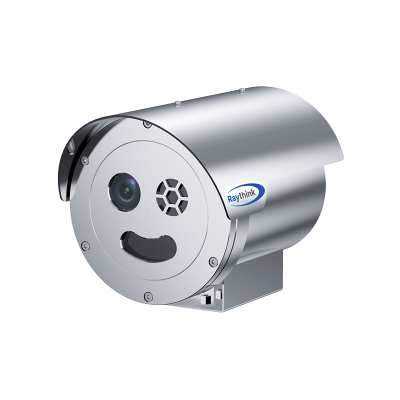
3) TN220 Thermographic Cube Camera

· 256×192 infrared resolution
· Precise temperature measurement
· Multi-protocol support for industrial and IoT system integration
· Powerful web client functionality
· Compact design
· PoE power supply support
· Dual-spectrum image display
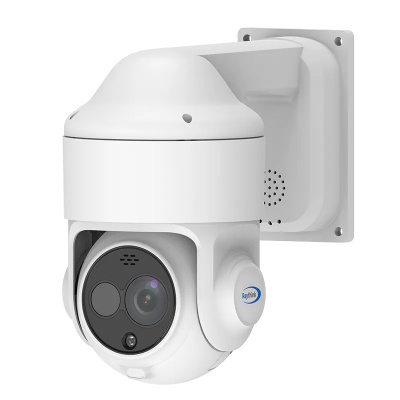
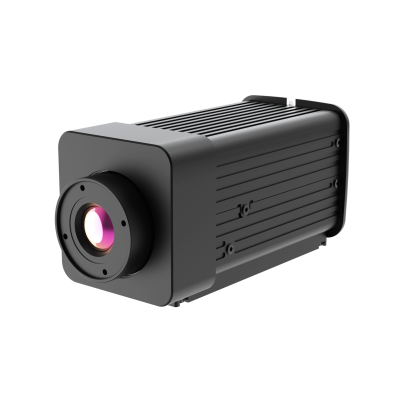
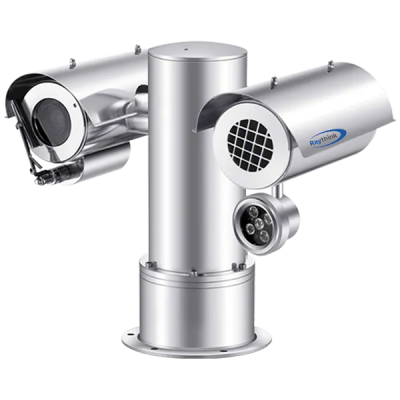
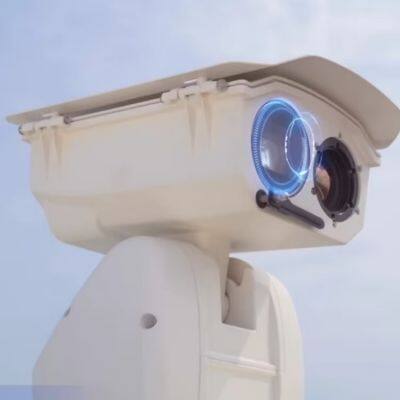
4) TN460 Fixed-mount Thermal Camera

· Next-generation imaging algorithm for sharper detail
· 640×512 infrared resolution for high-definition visuals
· <40mK NETD outperforming competing products
· -20°C to +650°C wide temperature measurement range
· 25Hz synchronized image and temperature frame rate
· Compact size, low power consumption, multiple lens options
· Rich interfaces supporting SDK development for easy integration
3. Advantages of Thermal Imaging Camera for Electronics Repair and Rework
· Non-Contact Detection
Thermal camera inspection requires no power shutdown, making operation convenient. Non-contact measurement leaves the original temperature field undisturbed, avoiding secondary damage or introducing new faults.
· Temperature Information Visualization
Clear imaging produces high-quality infrared thermal images, providing real-time temperature status of electronic components on circuit boards. Visualized temperature information effectively reveals the operational conditions of the circuit board.
· High Sensitivity for Detecting Subtle Temperature Differences
Thermal imaging cameras feature extremely sensitive temperature sensing capabilities. Measurements are stable with fast response speeds, detecting minute temperature variations. This allows identification of subtle thermal differences across electronic components to uncover potential faults.
· Powerful Temperature Analysis Software
The software intuitively displays real-time temperature distribution curves of inspection areas and stores images and video streams with temperature data. It supports diverse temperature measurement modes, including maximum/minimum temperature tracking, point/line/area temperature measuring, and configurable threshold alarms that trigger when temperatures reach preset ranges.
4. Application Cases in Electronics Repair and Rework
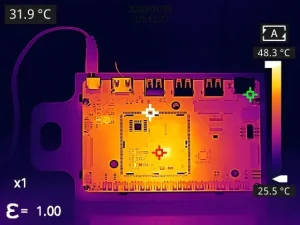
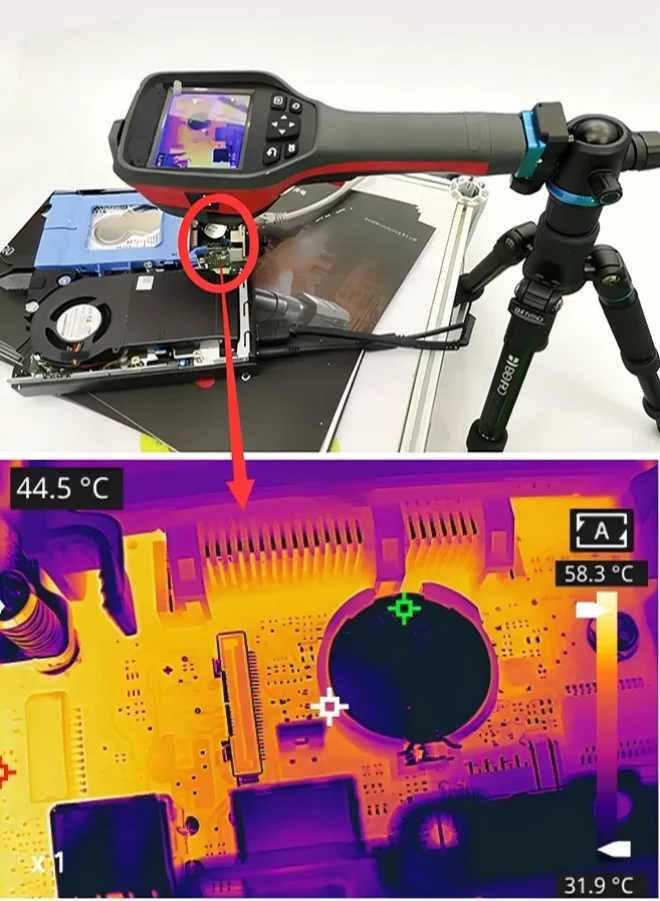
1) PCB Fault Localization
PCB (printed circuit board) is an indispensable component in electronic products. Most PCB faults result from component damage, such as chip defects, capacitor/resistor issues, or solder joint pin problems. Troubleshooting requires locating the damaged component for replacement. The traditional method involves using thermocouples for point-by-point temperature measurement and external converter boxes for data export, making the process cumbersome, inefficient, and prone to missed detections.
Since faulty components typically generate heat anomalies when powered on, thermal imaging can quickly identify abnormal areas based on temperature distribution, significantly improving localization efficiency.
Raythink Solution: Use handheld thermal cameras paired with professional temperature analysis software. The camera can be used for handheld patrol inspections or mounted on fixed brackets connected to external displays for monitoring.
· Thermal imaging directly displays component temperature distribution on the PCB, enabling intuitive identification of faulty components
· Manual precision focusing allows detection of targets as small as 1mm (at 0.1m distance), clearly observing the type and location of anomalous components

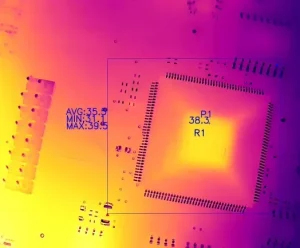
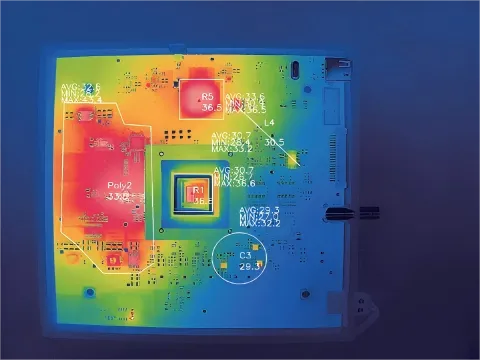
2) Circuit Board Design Testing Temperature Monitoring
During R&D phases, engineers must monitor the thermal load of components on circuit boards to evaluate the rationality of component layout design. Given the dense distribution of components on circuit boards, traditional contact-based temperature measurement not only involves complex procedures but may also disrupt the circuit’s own temperature field, failing to meet laboratory requirements for real-time multi-point data collection.
Combined with a constant-temperature chamber reaching 60°C to simulate actual circuit board operating environments, thermal imaging cameras provide visualized results of temperature distribution and thermal spot changes in electronic components. Engineers can use this data to identify potential risks and implement corrective measures accordingly.
Raythink Solution: Utilize an online thermal imaging camera to observe circuit boards while both are placed in a constant-temperature chamber. Field testing confirms the equipment operates reliably under 60°C conditions.
· Map critical inspection areas and obtain real-time temperatures of each electronic component
· Analyze collected temperature data to assess the current, voltage, and other parameters experienced by components
· R&D engineers precisely locate fault points based on detection results to optimize circuit design, thereby enhancing conversion efficiency, reducing internal temperature rise, and improving circuit reliability
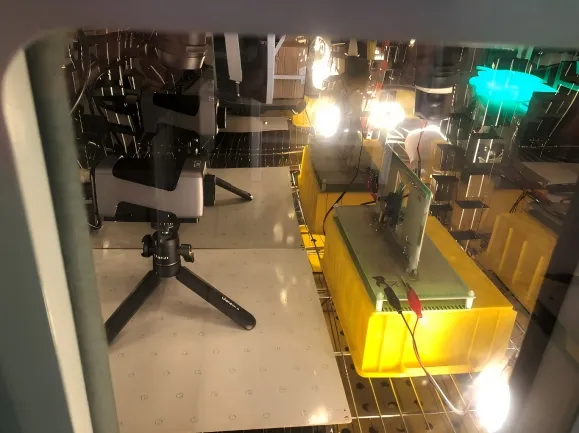



3) LED Chip Temperature Monitoring
LED chips may experience insufficient silver paste curing, contaminated brackets or chip electrodes during packaging and processing, causing high or unstable contact resistance. This results in localized chip temperature rise, affecting LED brightness, lifespan, or even causing failure. Traditional detection equipment struggles to meet inspection requirements for modern small-sized LED chips.
Thermal imaging cameras achieve precise imaging and temperature measurement through high sensitivity and macro lenses, particularly suitable for enlarged monitoring of small heat-generating areas. By clearly presenting temperature distribution, thermal imaging makes chip defect locations immediately apparent.
Raythink Solution: A thermal imaging camera deployed above the LED chip board monitors real-time temperature conditions in the chip core area. Paired with Raythink’s professional temperature analysis software TI Studio, it clearly reveals problems in the LED chip.
· Macro lens configuration combined with 1–8x digital zoom enables high-magnification clear imaging, precisely locating minute chip defects
· Multi-point temperature tracking and area analysis generate temperature thermal maps in real time, quickly locating high-temperature areas on the chip surface
· Automatic alarm settings through software automatically identify anomalous chips and generate detection reports, significantly improving detection efficiency

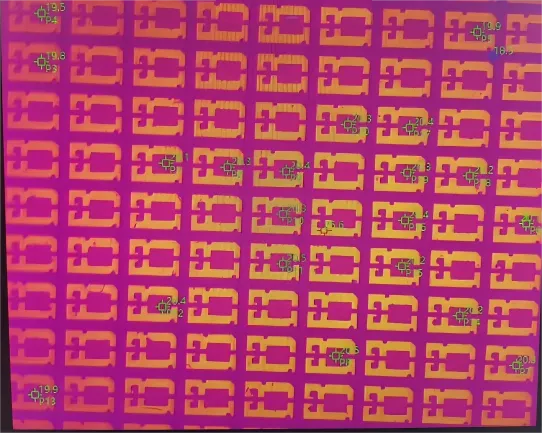
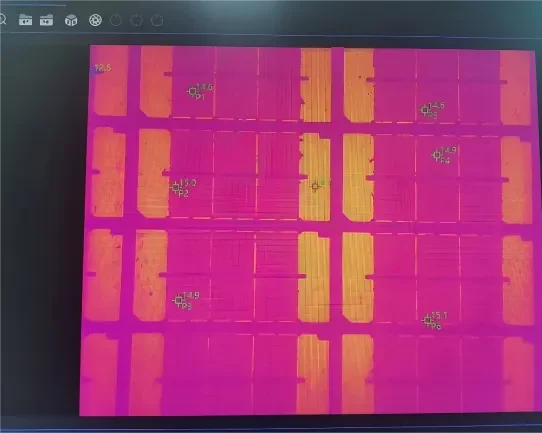
4) Battery Thermal Balance Testing
In current university research on materials and industrial control applications involving temperature measurement, monitoring and evaluating the thermal balance of batteries or battery packs is essential. Traditional thermocouple contact temperature measurement is cumbersome and can only monitor a single point on the battery, failing to meet the demand for large-scale data collection required in scientific research.
Infrared thermal imaging clearly reveals the temperature distribution patterns within batteries and battery packs, enabling evaluation of the effectiveness of battery pack heat dissipation structure design. This provides researchers with more efficient measurement tools, significantly accelerating the practical application of research findings.
Raythink Solution: Place target batteries requiring research into the battery testing temperature control system and adjust different temperatures via the constant-temperature control. Use a thermographic cube camera suitable for confined spaces to monitor temperature distribution across the entire surface of each battery group.
· The support for arbitrary point measurement on thermal images allows acquisition of any local temperature within the thermal camera’s coverage area
· Point selection at different locations enables tracking of maximum and minimum temperatures
· Overlay of digital photos with complete thermal images provides more detail for image analysis, facilitating comprehensive evaluation and monitoring battery temperature development trends. This provides data support for battery thermal balance research
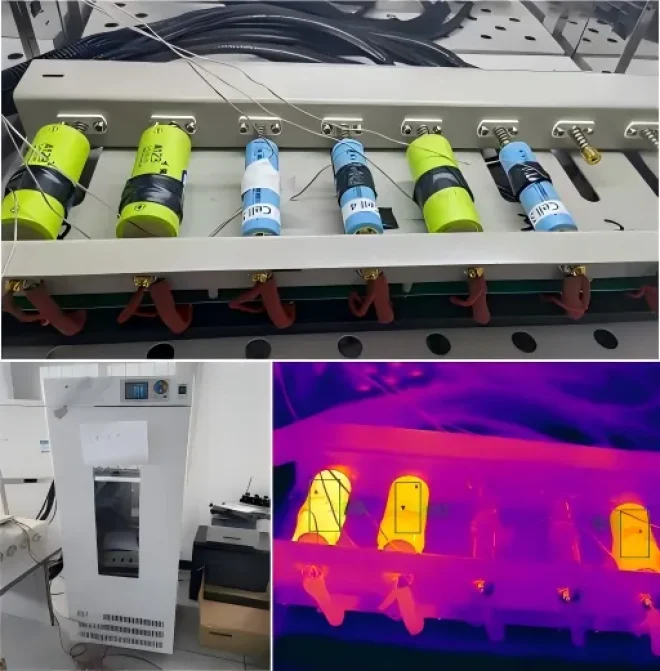

5) Battery Case Leakage Detection
Batteries risk leakage under conditions such as poor welding, damaged plates, or structural defects. Mild cases result in performance degradation, while severe cases may trigger safety incidents. Common detection methods such as resistance testing, gas pressure testing, VOC analysis, or visual inspection often fail to directly identify the leakage location and severity. They also lack efficiency, and are susceptible to human judgment.
Thermal imaging cameras capture temperature differences formed by the leaking liquid on the battery surface, efficiently and accurately identifying the locations and scope of battery leakage. Thermal imaging inspection requires no battery disassembly and can simultaneously cover large surface areas.
Raythink Solution: Deploy an online thermal camera to monitor surface temperature distribution on battery cases, paired with professional analysis software to set leakage characteristic temperature ranges for automatic marking and alarm.
· The thermal camera rapidly scans the entire battery case surface, precisely pinpointing leakage points through temperature anomalies, significantly reducing inspection time
· Area temperature measurement function quantitatively assesses leakage parts, determining severity and scope to distinguish minor seepage from severe leaks, and guiding different handling strategies accordingly
· The support for long-term data storage and offline analysis allows the establishment of a thermal characteristic database for battery leakage, assisting factories in leakage failure mode analysis

5. Tips for Using a Thermal Camera for Electronics Repair and Rework
· Ensure Proper Focus and Lens Selection
Electronic components are typically small, making proper focus and appropriate lens configuration critical. Based on different inspection targets and working distances, select standard lenses, macro lenses, or super-macro lenses to ensure clear imaging.
· Control Inspection Environment Conditions and Component Operating States
Maintain a relatively stable inspection environment, avoiding direct sunlight or strong heat sources. Electronic components should be powered and run to thermal equilibrium before inspection to fully reveal heating faults while maintaining stable circuit operation, avoiding misjudgment caused by transient temperatures.
· Compare Thermal Images of Normal and Suspected Electronic Components
Under identical operating conditions and ambient temperatures, use thermal images of normal components of the same model as reference baseline. Comparing these against the thermal images of components under test allows intuitive detection of anomalous areas through temperature distribution differences, even without professional expertise.
· Reasonably Set Thermal Camera Temperature Parameters
Adjust parameters such as emissivity according to the material characteristics of inspection targets, ensuring accurate infrared temperature measurement. Also, leverage the software’s alarm threshold function to preset abnormal temperature ranges, automatically marking problem areas.
· Preserve Raw Data for Analysis
Record thermal imaging videos or save high-quality thermal images for subsequent in-depth analysis and problem tracing. Combined with temperature curve records, this enables more accurate diagnosis of electronic component faults.
· Clean the Lens and Perform Regular Maintenance
Dust, fingerprints, or condensation on the lens severely impact infrared radiation reception, resulting in inaccurate temperature measurement. Regularly wipe lenses with specialized lens cleaning cloths and solutions, avoiding rough materials or strong chemicals that may damage the lens.
6. Conclusion
Thermal imaging technology makes the temperature behavior of electronic devices visible and quantifiable, enabling technicians to rapidly identify fault points and potential risks during R&D, testing, and repair processes. It not only improves troubleshooting efficiency and diagnostic accuracy but also helps optimize circuit design and reliability verification. Raythink, leveraging professional infrared temperature measurement technology and mature application experience, provides efficient thermal detection solutions for the electronics industry, addressing end-to-end needs from design verification and production testing to fault repair. To explore thermal imaging inspection solutions tailored to your business, contact Raythink’s technical team for personalized one-on-one consultation.
Recently Posted
-
Outdoor Commercial Security Cameras: What You Need to Know
January 28, 2026In today's complex security landscape, outdoor areas of commercial properties face challenges such as theft, vandalism, survei Read More
Read More -
Four Core Scenarios: Infrared Thermal Camera Safeguards New Energy Underground Parking Facilities
January 27, 2026With the surge in the number of new energy vehicles, the fire safety risks of underground parking facilities have become increasin Read More
Read More -
Non-Contact Temperature Measurement in Biological Research via Infrared Technology
January 26, 20261. Background IntroductionIn biological mechanism research such as animal metabolic behavior analysis, body temperature serves as Read More
Read More -
Infrared Thermal Camera for Temperature Visual Monitoring in Logistics Cold Chain Vehicles
January 22, 2026Temperature monitoring during refrigerated truck transportation is a key application of thermal cameras in cold chain logistics. D Read More
Read More























